Image: Shutterstock
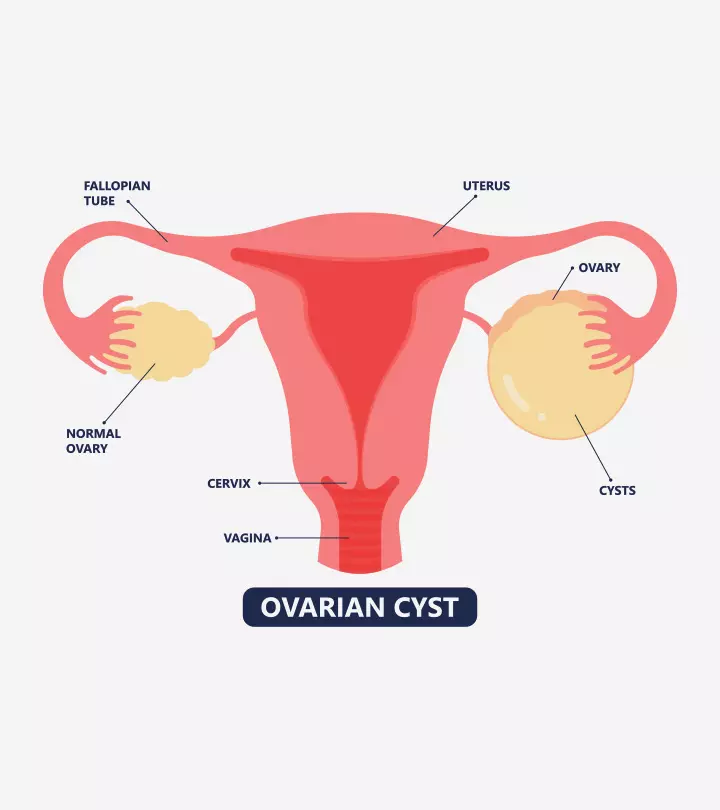
Ovarian cysts or ovarian masses are benign and harmless fluid-filled structures formed during the menstrual period every month. However, ovarian cysts during pregnancy may have developed in the pre-pregnancy period and continued to grow throughout the pregnancy.
The size of these cysts could range from one centimeter to more than ten centimeters in diameter, but they are harmless and quite common in women. However, sometimes, ovarian cysts may twist and rupture during delivery. In rare cases, they turn malignant or cancerous and may require medical care (1) (2).
Read this post to learn about the causes of ovarian cysts during pregnancy, the symptoms of being pregnant with ovarian cysts, and the treatment options available.
What Are Types Of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts can be of different types depending on their clinical features (1) (3).
1. Functional cysts
These are the most commonly found ovarian cysts and are typically benign. The functional cysts can further be classified into two categories.
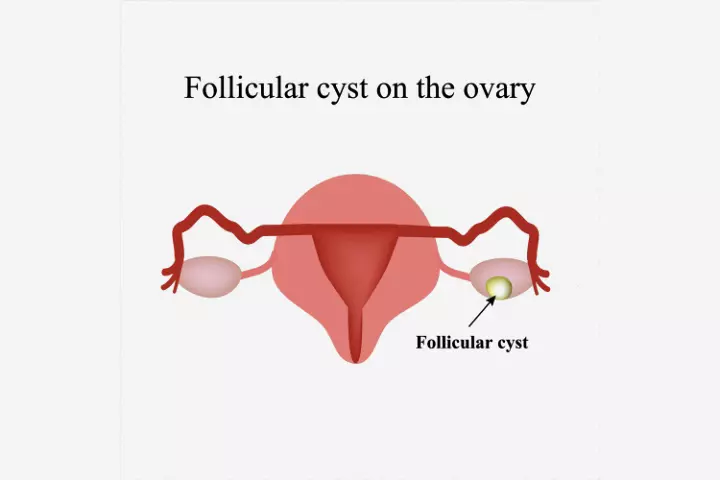
- Follicle cyst: The follicle on the ovary is a sac that contains the egg. During ovulation, the follicle breaks open and releases the egg. It develops into a follicular cyst when it fails to break open to release the egg, and fluids accumulate inside the follicle. A follicular cyst does not require any treatment and heals on its own within three months.
Image: Shutterstock
- Corpus luteum cyst: Following the release of the egg, the follicle contracts into a structure called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum starts to release hormones, such as progesteroneiA female reproductive hormone that plays a vital role in menstruation, pregnancy, and breastfeeding. , to prepare the body for pregnancy. Corpus luteum cyst develops when the follicle does not contract and seals immediately after releasing the egg. This leads to fluid accumulation.
2. Teratoma
Teratoma is usually composed of various tissues such as skin and hair.
This type of ovarian cyst develops at birth. However, it might show signs of growth at the menarcheiThe time when a woman experiences her first period. stage of a woman’s life and continue to grow till menopause.
3. Dermoid cyst
They are congenitaliExisting right from birth. . Dermoid cysts are composed of tissues that make up the hair, skin, and teeth. Dermoid cysts are mostly benign and do not show any symptoms.
Charleston Crafted, who received a diagnosis of a dermoid cyst during her pregnancy, was recommended to undergo laparoscopic surgery. She reflects, “One of the weirdest things about this whole thing was that I had no symptoms, no swelling, no pain, and no bleeding. I felt fine. I don’t know if it’s hard for doctors, but as a non-medical person, it is hard to have no symptoms and sign up to go get surgery to fix something that you can’t see (i).”
4. Cystadenoma cyst
These cysts grow outside the ovary from its outer lining tissue and are mostly benign. Cystadenoma are multilocular cysts and are filled with fluid-like mucus.
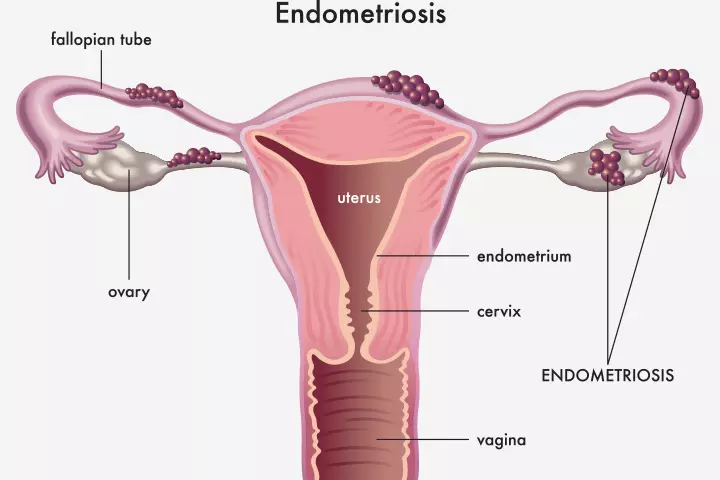
5. Endometriomas
Image: Shutterstock
Endometrioid cysts spring from endometriosis, a condition where the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium) starts to grow outside the uterus. According to the World Health Organization, this condition affects around 190 million women and girls of reproductive age.
 Point to consider
Point to considerWhat Causes Ovarian Cysts During Pregnancy?
Ovarian cysts occur during the menstrual cycle and can persist throughout pregnancy. Ovarian cysts during pregnancy can be caused by any of the following factors (4) (5).
- After the egg is released from the follicle, rather than contracting into the corpus luteum, it seals itself back, and fluid begins to accumulate inside it. This leads to the development of a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy. These cysts mostly subside towards fourteen to sixteen weeks of gestation without posing any threat to the expecting mother’s
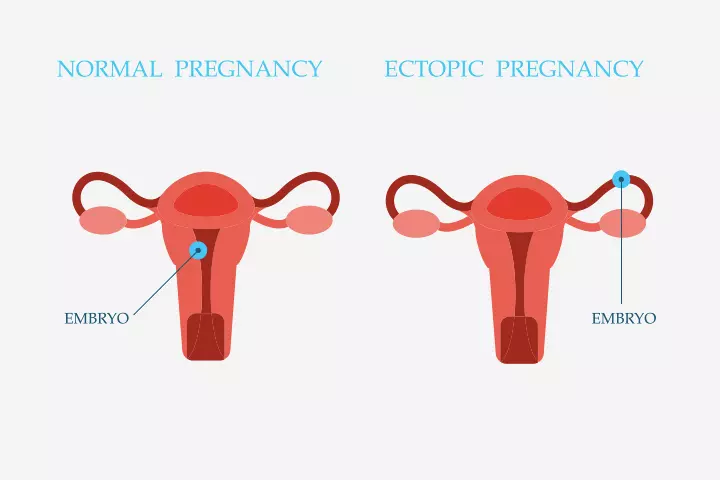
- Ectopic pregnancy, a condition where the egg adheres to the outside of the uterus, could also lead to cyst formation during pregnancy.
Image: Shutterstock
- Another type of benign tumor called thecaiThe layer of cells surrounding an ovary's egg-producing follicles, playing a crucial role in follicle development and ovulation. lutein cyst could also be seen during pregnancy. It mostly arises due to increased levels of hCG and is more common in the case of twin pregnancy.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ovarian Cysts?
Generally, ovarian cysts do not show any symptoms. However, certain symptoms, at times, become noticeable (1) (6).
- Pelvic pain and faint backaches
- A swollen or overblown abdomen
- A sense of pressure or pain in the bowel or while defecating
- Pain during urination
- In case of a ruptured cyst, swollen abdomen with severe pain
- Abnormal or painful periods
Image: Shutterstock
What Are The Complications Of Ovarian Cyst?
Most ovarian cysts during pregnancy are benign and may show no symptoms. However, if the cyst continues growing through pregnancy and even until childbirth, there could be a risk of the ovarian cyst getting ruptured. A condition called ovarian torsion might also occur where the cyst weighs the ovary down, causing it to twist.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) could be at a high risk of developing high blood pressure, premature delivery, and miscarriage. Regular doctor visits could help avail the right treatment at the right time (7).
Is It Safe To Remove An Ovarian Cyst During Pregnancy?
There is usually no need to remove ovarian cysts during pregnancy. The corpus luteum cyst produces pregnancy hormones to support the pregnancy and goes away on its own after a few weeks of pregnancy. However, certain cysts, such as ectopic pregnancy cyst, may require surgical removal.
In case a cyst starts to ooze blood or imparts pain, a laparoscopic surgery might be recommended. Here, the cyst is removed via a small cut made in the abdomen. Your healthcare provider will weigh the risks and benefits of cyst removal to your and your baby’s health before proceeding with a procedure.
Can An Ovarian Cyst Burst During Pregnancy?
Generally, an ovarian cyst rupture does not pose a threat to the expecting mother’s health or the baby. It usually fades away with time and might not require any medical interference. However, under certain conditions, it could lead to various complications.
Sometimes, ovarian cysts may form in response to an infection, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). In PID, sexually transmitted bacteria infect any one or more of the reproductive organs. If such an infected cyst ruptures, it could become fatal and lead to septicemiaiThe body's most extreme response to an infection characterized by bacteria entering the bloodstream. . Under such conditions, doctors might recommend taking antibiotics or surgery, depending on the severity of the infection (8).
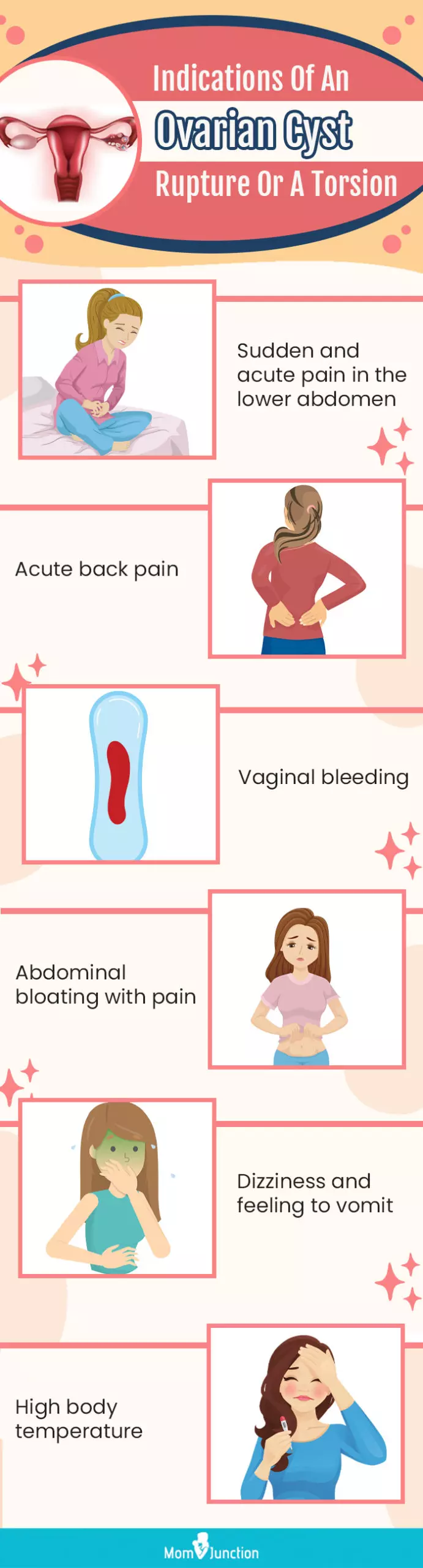
How To Know You Have An Ovarian Cyst Rupture?
Some of the symptoms indicating an ovarian cyst rupture might include (8):
- Unexpected and acute pain in the lower abdomen and the back
- Bleeding from the vagina
- Abdominal bloating is accompanied by a sharp pain
- Dizziness and tendency to vomit
- High body temperature
How To Know You Have An Ovarian Cyst Torsion?
Ovarian cyst torsion refers to the state of an ovary, or sometimes the fallopian tubes when they twist on the tissues surrounding the ovary. This leads to the obstruction of blood flow to the ovary. Immediate surgery is the only accepted treatment in order to avoid the loss of an ovary.
The symptoms of ovarian cyst torsion include (9):
- Random and acute abdominal pain
- A sense of vomiting and dizziness
 Quick fact
Quick factDo Ovarian Cysts Affect Fertility?
Ovarian cysts usually do not affect fertility. However, ovarian cysts developed due to certain health conditions could lead to complications in pregnancy (3) (7).
- Endometriosis:It refers to the condition where the inner lining of the uterus starts to grow on the outside of the uterus, such as on the ovary. A cyst formed due to endometriosis can affect fertility.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): It refers to a condition where multiple cysts develop on the ovary. The presence of PCOS makes it difficult for the ovary to produce female hormones and release eggs from the follicles, affecting a woman’s health. Cysts developed as a result of PCOS may lead to infertility. Furthermore, the hormonal imbalance in PCOS increases the risk of gestational diabetes.
How Are Ovarian Cysts In Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Ovarian cysts can be diagnosed via different tests and medical exams (1).
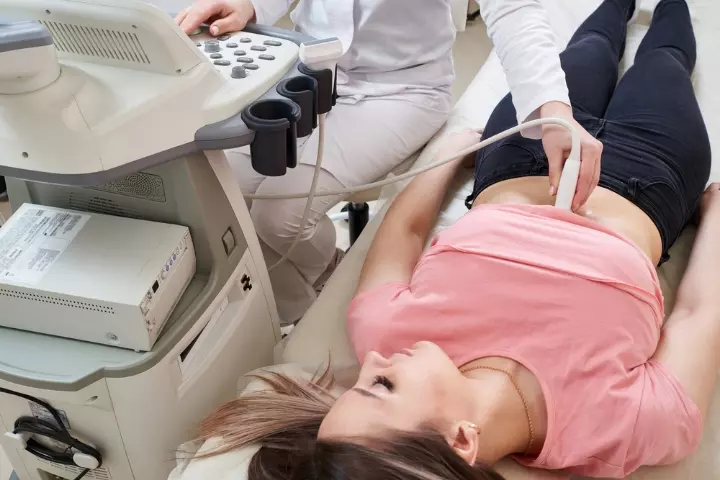
- Ultrasound: An endovaginal or transvaginal ultrasound is carried out to view any abnormality in the reproductive organs. This method makes use of a device called a transducer, which produces sound waves. The transducer is positioned in the vagina, and the sound waves help locate and visualize the cyst.
Image: Shutterstock
- Blood test: Your OB-GYN may also carry out blood tests to detect the level of CA 125. Test for CA 125, besides ultrasound, is carried out to determine if there is any risk of the ovarian cyst turning cancerous. CA 125 is a protein in the body that acts as a tumor marker. An increased level of tumor marker could indicate ovarian cancer, especially in menopausal women.
How Are Ovarian CystsTreated?
Ovarian cysts with no symptoms generally require monitoring with no specific treatment. Ovarian cysts with symptoms and recurring ovarian cysts could require treatment (3) (10). The mode of treatment may vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and your general health.
Medication might be prescribed to reduce the size of the cyst initially, and many women may find relief from symptoms. However, if the cyst continues to grow and causes extreme pain and bleeding, the doctor might suggest surgery through any of the following methods.
- Laparoscopy: It is mostly carried out for cysts that are benign. A small cut is made in the lower abdomen, and a tube fitted with a camera is slid through the cut to view and remove the cyst.
- Laparotomy: Here, the doctor makes a bigger cut in the abdomen for the removal of the cyst. It is usually carried out for cysts that appear to be malignant.
 Quick fact
Quick factYour doctor may prescribe additional tests before or after the procedure to check the health of the baby and to determine any cancer markers (1) (11).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which food should I avoid in ovarian cyst during pregnancy?
Researchers have proven that some ovarian cysts are more common in women who consume beef, other red meat, and cheese. But, high consumption of green vegetables may have a protective effect (12).
2. Is vaginal delivery possible with an ovarian cyst?
Pregnant women with giant ovarian cysts can go for a vaginal delivery unless there are other indications for cesarean sections. Post delivery, the cysts can be managed laparoscopically (13).
3. Can stress or emotional factors contribute to the development of ovarian cysts during pregnancy?
No direct evidence links stress or emotional factors to the development of ovarian cysts during pregnancy. Ovarian cysts are typically formed as a normal part of the ovulation process and can occur independently of emotional factors.
4. Are there any specific exercises or physical activities that should be avoided with ovarian cysts during pregnancy?
Consult your healthcare provider for guidance on exercise and physical activities during pregnancy with ovarian cysts. As a general caution, you may want to avoid high-impact and strenuous exercises, focusing on low-impact options like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga. Listen to your body and make modifications as needed.
Ovarian cysts during pregnancy may not cause any problems if the size remains the same. A growing cyst can cause ovarian rupture or ovarian torsion, or twisting. Large cysts may also obstruct the abdomen or pelvis and complicate pregnancy and childbirth. Pain and pressure in the abdomen are common signs of ovarian cysts. Ultrasound and blood tests are ordered to confirm ovarian cysts’ diagnosis, type, and risks. Growing or larger cysts that could interfere with pregnancy and delivery can be surgically removed during pregnancy.
Infographic: Possible Signs Of Rupture Or Torsion Of An Ovarian Cyst
After a miscarriage, it may not be easy to return to good health and plan for the subsequent pregnancy. So, it is essential to seek medical help and take utmost care of yourself. Also, follow the precautionary steps discussed below to avoid the risk of complications in future pregnancies.
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Key Pointers
- An ovarian cyst may cause pain during urination, swelling in the abdomen, and backaches.
- The burst of an ovarian cyst may sometimes cause an infection.
- The treatment plan for an ovarian cyst during pregnancy depends on the type of the cyst.
- Medications, laparoscopy, or laparotomy are a few methods used to treat an ovarian cyst.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My experience having a dermoid ovarian cyst removed during pregnancy.https://youtu.be/ZZXmYucv4N8
References
- Ovarian Cysts.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/ovarian-cysts - Ovarian Cysts.
https://www.foxchase.org/blog/qa-about-ovarian-cysts - Ovarian Cysts.
https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/ovarian-cysts - J. de Haan et al. (2015); Management of ovarian cysts and cancer in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4402440/ - Theca lutein cyst.
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/theca-lutein-cyst - Ovarian cysts.
https://www.bcm.edu/healthcare/specialties/obstetrics-and-gynecology/ob-gyn-conditions/ovarian-cysts - Ovarian cyst and pregnancy: Could a cyst stop me from having baby;
https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/fertility-blog/2016/august/ovarian-cysts - What risks are associated with a ruptured ovarian cyst?;
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/what-risks-are-associated-with-a-ruptured-ovarian-cyst - Ovarian Torsion;
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/ovarian-torsion - Ovarian cyst;
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001504.htm - Diagnosis and management of adnexal masses;
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2009/1015/p815.html - Francesca Chiaffarino, et al.; Diet and risk of seromucinous benign ovarian cysts.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12969583/ - Saeed Marzoq Baradwan; Giant ovarian cyst in pregnant woman had uncomplicated term vaginal delivery and treated laparoscopically postpartum: A Case Report.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319472202_Giant_ovarian_cyst_in_pregnant_woman_had_uncomplicated_term_vaginal_delivery_and_treated_laparoscopically_postpartum_A_Case_Report# - Sheela S. R. et al.; (2017); Obstetric outcome in pregnancy complicated by ovarian cysts.
https://www.ijrcog.org/index.php/ijrcog/article/download/3660/2972 - J. de Haan et al.; (2015); Management of ovarian cysts and cancer in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4402440/
Read full bio of Dr. Prachi Benara
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Reshmi Das