Image: ShutterStock
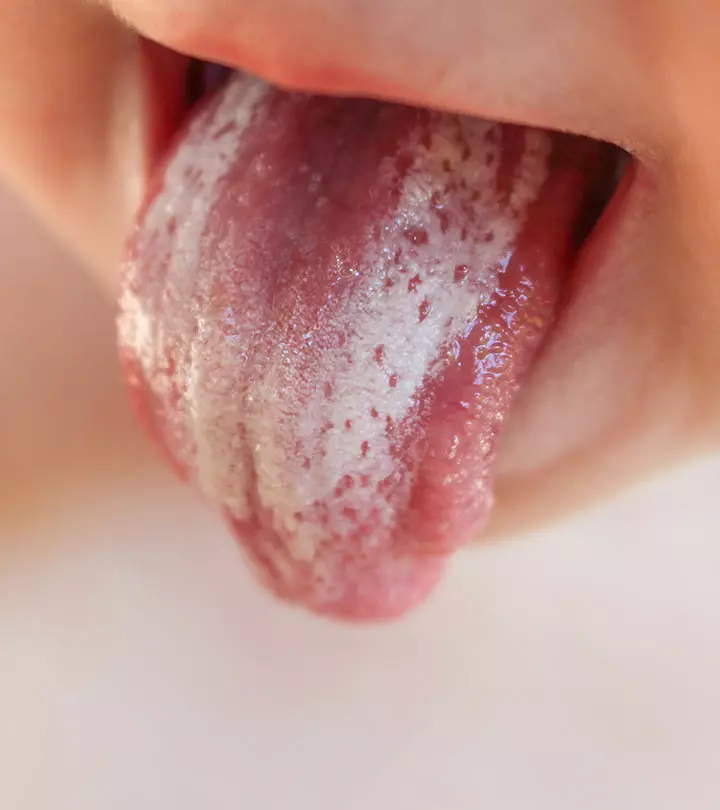
Frequent sores in the mouth or complaints about difficulty in swallowing food may indicate thrush in children. Also known as oral candidiasis or oral thrush, it is one of the most common fungal infections caused by the yeast Candida Albicans that may affect children. If the child is healthy otherwise, thrush is usually not a cause of concern. Read this post as we tell you about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, complications, home remedies, treatment, and prevention of oral thrush in children.
What is Thrush?
Thrush is a fungal infection of the mouth and is caused by the yeast Candida albicans(1)
. It can affect the tongue, throat, gums, or the lining of the mouth, causing irritation. Thrush is also called oral candidiasis or oral thrush.
The yeast Candida is a microorganism naturally present inside the body. It grows at a normal rate in the mouth, throat, or esophagus without causing any symptoms. But if the environment inside the mouth becomes favorable for excessive growth of this microorganism, it can lead to an infection (2).
The next section lists the signs of thrush you must look for in your child.
What Are The Symptoms Of Thrush?
If your child complains of discomfort or pain in the mouth, then check for these symptoms (3) (4):
- White spots or patches on the lips, tongue, and inner cheek.
- Scraping the white patch reveals the redness or red spots, which may bleed.
- Sore mouth and throat.
- Cracks and fissures in the mouth.
- Difficulty in swallowing food.
- Loss of taste.
- Feels like there is cotton in the mouth.
The section below lists the risk factors causing thrush in children.
What Are The Causes Of Thrush?
Here are the factors that can increase the chances of thrush in children (4):
- Result of an antibiotic treatment that destroys the balance of microorganisms within the body.
- Weakened immune system due to prolonged illness or health conditions like HIV, cancer or cancer treatments, or congenital immune deficiencies.
- Conditions causing dry mouth.
- Use of medications for treating psychiatric conditions.
- Use of corticosteroids for the treatment of inflammation or asthma can cause oral thrush. This is seen more often if an inhaled cortisone is used without a spacer device
- Diabetes with high blood sugars
Early diagnosis of the condition helps in taking the right step towards treatment.
 Quick tip
Quick tipHow Is Thrush Diagnosed?
The pediatrician will first examine the child for the symptoms of thrush. Further, a small sample will be collected by scraping the lesion inside the mouth for microscopic examination. It helps to identify the type of yeast infection and its sensitivity.
The below section explains the different medications used in treating thrush.
 Point to consider
Point to considerWhat Is the Treatment For Thrush?
Mild thrush generally does not require any treatment as it clears on its own. But if the symptoms do not subside, then the doctor may prescribe the following treatments:
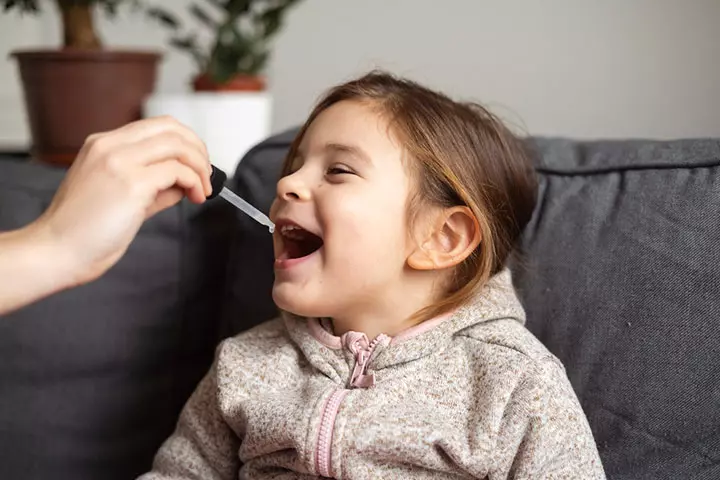
- Antifungal oral gel: The doctor may prescribe an anti-fungal oral gel that needs to be applied to the affected area in the mouth, using a cotton swab. It needs to be done at least four times a day. Make sure not to feed the child for 30 minutes after applying the medicine. The medicine has to be used for seven days and continued for three more days after the thrush disappears (5).
Dosage:
1mL for one-month-old babies and 2mL for children aged over a month
If you are breastfeeding your baby, your nipples might become infected and cause itching. It is wise to apply the oral gel also on your nipples before and after breastfeeding, to stop re-infection between mother and baby. If you’re experiencing nipple discharge, it may be a sign of a yeast infection; hence, getting it tested to identify the cause and solution is important.
- The doctor may also prescribe an anti-fungal drop that needs to be given to the child after every meal for up to 10 days (6).
- Nystatin (Antifungal mouthwash) is commonly prescribed for thrush in children. Other medicines include clotrimazole (Lozenges), fluconazole (Diflucan), and itraconazole (Sporanox). The last two are available as pills or syrups. (7).
If you find any unusual symptoms along with thrush, then call your doctor right away.
When To Call A Doctor?
When thrush becomes severe, the child may show other symptoms too. Watch out for these symptoms and seek medical assistance if your child has them (5) (6):
- The child looks unwell and has a fever.
- Extremely dry mouth.
- Painful lesions develop inside the mouth.
- The infection becomes recurrent even after taking the medication.
- Dark urine or very less urination in 8 hours.
- Drinking less water.
- Bleeding in the mouth.
Mild thrush can be managed with a few home remedies.
Home Remedies For Treating Thrush
Here are a few home care tips to prevent thrush and alleviate its symptoms in children:
- Use a soft toothbrush for brushing the teeth.
- Use warm salt water to rinse the mouth.
- Let the child eat unsweetened yogurt while taking medicines for thrush.
- Lactobacillus supplements help maintain the balance of Candida in the mouth.
- Eating cold food and drinking cold liquids can ease the discomfort of thrush. Also, eating soft and easy-to-swallow food can lessen the discomfort of thrush.
Thrush is usually curable. But in the case of a weakened immune system, there are chances of re-occurrence, which may cause serious problems (7). It can also cause invasive illness in immunocompromised patients.
Complication Of Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is rarely dangerous but can be unpleasant. If the fungus spreads into the food pipe, then it makes swallowing difficult. Severe untreated thrush can also spread to the esophagus, urinary tract, or the whole body causing an infection that can lead to multiple organ failure and death (4).
However, if it is left untreated for years, then the fungus can penetrate, although rarely, deeper into the tissue layers and enter the bloodstream, resulting in blood poisoning (septicemia), which is also life-threatening (1).
Preventive measures can stop the overgrowth of the fungus that leads to such complications. Find out more about it in the next section.
How To Prevent Oral Thrush?
Here are a few tips you can follow to prevent thrush:
- Avoid using mouthwash.
- Maintaining proper oral hygiene.
- Rinsing the mouth thoroughly after the child uses a corticosteroid inhaler.
- If your baby uses bottles and a pacifier, make sure to sterilize this properly. Washing it with coarse salt might also help.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. At what age is thrush common in children?
Thrush can affect children at any age; however, it is the most common in infants younger than six months (8).
2. Is thrush contagious in children?
Thrush may be contagious to children with weak immune systems or those under certain medications. While it is unlikely to spread through physical contact among healthy children, activities like sharing toys or pacifiers or close contact with each other’s saliva can facilitate the transmission of thrush (9) (12).
3. How long does it typically take for thrush in children to clear up with treatment?
The duration of treatment for thrush in children may vary. With appropriate antifungal medication, improvement is usually seen within 4 to 5 days; however, you should continue the medications for the recommended time period (12).
4. How can parents and caregivers differentiate between thrush and other oral health issues in children?
It can be challenging for parents and caregivers to differentiate thrush from other oral health issues in children. If parents are unsure about the condition by seeing the physical characteristics, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is advisable.
Oral thrush is one of the most common fungal infections in children. Children with oral thrush may be irritable, cranky, and may have trouble swallowing, among other symptoms. Children with weakened immune systems may be more prone to developing these infections. The complications of thrush in children include severe infections that could affect multiple organs. However, quick diagnosis and treatment can aid in faster healing and better prognosis. Hence, do not ignore the appearance of thrush, even if it is a small lesion, to avoid any major complications.
Infographic: Home Remedies For Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is a common infection in children and may cause difficulty swallowing and soreness in the affected area. While thrush can be treated with medication prescribed by a doctor, there are also several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms and speed up the healing process. This infographic lists a few of the effective ones. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
This video will discuss Oral Thrush, also known as Candidiasis or a yeast infection. It can cause painful sores and cracks in the corners of the mouth, known as Angular Cheilitis.
Key Pointers
- Candida albicans causes thrush, a fungal infection that affects the mouth and tongue.
- A child can become susceptible to this infection due to a weakened immune system, certain medications, and diabetes.
- Common symptoms of thrush in children include white patches on the tongue and inside of the mouth, loss of taste, soreness, and difficulty swallowing.
- Doctors can prescribe antifungal medications such as nystatin or fluconazole to treat thrush.
- Seek medical treatment if you suspect your child has thrush as untreated thrush can lead to more serious health problems.
References
- Oral thrush (oral candidiasis): Overview; NCBI
- Oral candidiasis; DermNet NZ
- Thrush—Child; Winchester Hospital
- Symptoms of Candidiasis; Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
- Thrush; Children’s Hospital Colorado
- Oral thrush; Raising Children Network (Australia)
- Thrush – children and adults; NIH
- Oral Thrush; Nemours Kids Health
- Thrush; Cleveland Clinic
- Thrush (Oral Candida Infection) in Children; University of Rochester Medical Center
- Thrush – children and adults; MedlinePlus
- Thrush and Yeast Infections; Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Read full bio of Dr. Elna Gibson
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Ghazia Shah