Dyspepsia or indigestion in children can be a symptom of several underlying conditions. Children of any age can experience this problem, and indigestion can be occasional or regular, depending on its cause.
If your child has been experiencing regular indigestion, it is important to seek a doctor’s advice to understand the cause. Read on to know more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pediatric dyspepsia.
What Are The Symptoms Of Indigestion In Kids?
Indigestion itself is not a disease. In some cases, it can be a symptom of an underlying condition. Duration and the associated symptoms may vary depending on the cause.
The following signs and symptoms are common during indigestion (1):
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bloating
- Burping (belching)
- Gurgling or churning stomach
- Acid reflux
- HeartburniA common discomfort caused due to reflux of stomach contents to the food pipe, marked by a burning sensation in the chest that can be felt as a burning sensation or feeling in the chest with a sour or bitter taste in the mouth
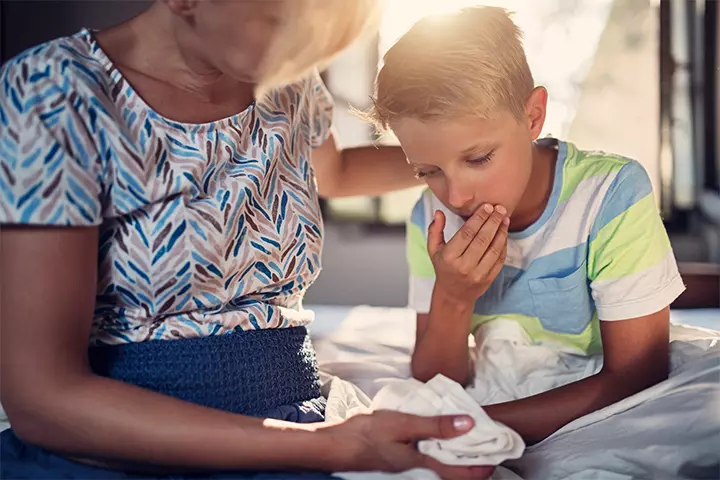
- Nausea or vomiting
Image: IStock
- Diarrhea
- Intestinal gas and feeling of fullness
The intensity, duration, and type of symptoms may vary in each child. Usually, these symptoms may last for several hours after a meal.
Seek emergency care if your child has any of the following severe symptoms of dyspepsia (1):
- Swallowing difficulties
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Hematemesis (vomiting of blood) or “coffee grounds” vomit
- Continuous vomiting
- Cold sweats
- Melena (black tarry stools) due to bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Indigestion may feel like stomach cramps/aches or stomach upset. This may be similar to other difficulties of the upper abdomen. Therefore, it is suggested to seek medical care for frequent indigestion and if your child has any severe symptoms.
Causes Of Indigestion In Children
Indigestion can be caused by the intake of certain foods or due to some conditions. If there is no known cause for indigestion, then it is referred to as functional dyspepsia.
The following foods and factors may cause indigestion in kids (2):
- Fast eating
- Overeating or eating a large meal
- Spicy food
- Fiber-rich foods
- High fat or oily foods
Image: Shutterstock
- Eating late at night
- Caffeinated or carbonated drinks
- Chocolates
- Not sleeping well
- Certain medications such as antibiotics, iron supplements, aspirin, and ibuprofen can cause medication-induced dyspepsia
- Stress and anxiety
- Secondhand smoke
Consult a pediatrician if your child’s medications or supplements are causing indigestion. They may give alternatives or other drugs to prevent it.
The following diseases and conditions can also be a cause of several gastrointestinal problems and severe indigestion in children (3):
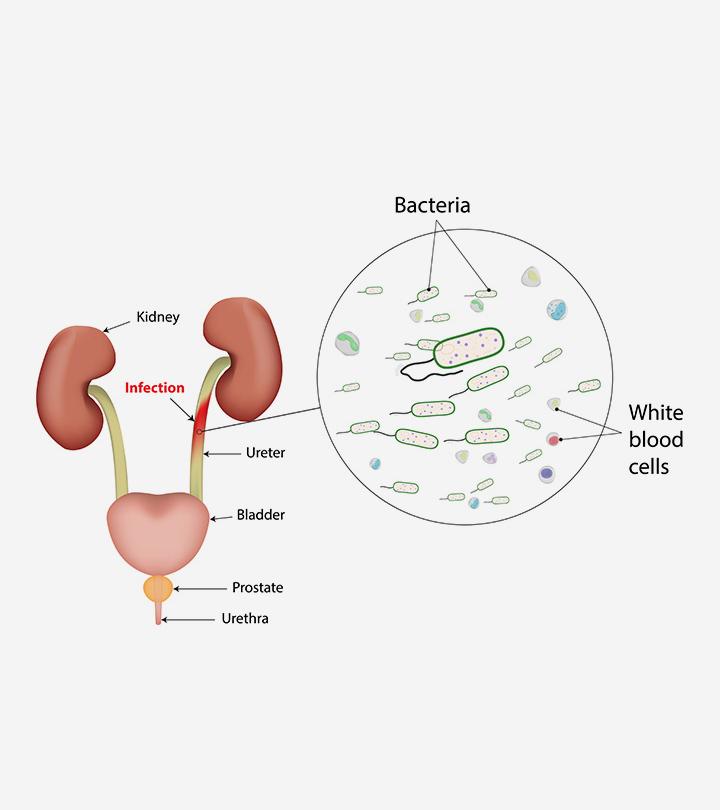
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or acid reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux is a condition where stomach contents regurgitate into the esophagus. According to a systematic review conducted by multiple institutions, GERD is present in about zero to 38% of all children older than 18 months. The presence of GERD can cause heartburn and other symptoms of indigestion.
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach may cause indigestion.
- Peptic ulcer: Sores or ulcers in the stomach can cause digestive problems.
- Infections: Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection may result in indigestion.
- Gastroparesis: This condition affects the motility or movement of the stomach. Motility disorders of the stomach can slow down the movement of food and often result in poor digestion or indigestion.
- Celiac disease: It is also known as gluten enteropathy or celiac sprue, which is an immune disorder causing gluten sensitivity. Indigestion can be one of its symptoms (4).
- Intestinal obstruction: Bowel obstruction may cause indigestion and intestinal discomfort.
- Stomach cancers: This is rare in children, but gastric cancers may be a cause.
Dyspepsia due to diseases can be frequent, and this requires medical care for treatment.
When To Call A Doctor
If your child has severe symptoms of indigestion, then you should seek immediate attention. Frequent indigestion requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. If your child has indigestion after consuming certain foods and medications, then you may mention it during the pediatric visits.
 Be watchful
Be watchfulDiagnosis Of Indigestion In Children
After analyzing your child’s symptoms and physical examinations, the doctor may order the following tests for diagnosis (5):
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- Stool or breath tests
- Ultrasound
Image: Shutterstock
- X-ray or CT scan
- Upper endoscopy or esophagogastroscopy is the visualization of the upper gastrointestinal tract using a thin, flexible tube.
Laboratory analysis of blood and urine can be useful to identify infections and metabolic disorders
. Confirmation of Helicobacter pylori infection can be obtained from stool or breath tests. Imaging tests help visualize the upper digestive tracts and may help diagnose ulcers, obstruction, and cancers.
How To Treat Indigestion In Children?
Treatment of indigestion can vary depending on the causing factor or disease. If the causes are dietary factors, stress, or lack of sleep, then avoiding them could prevent indigestion.
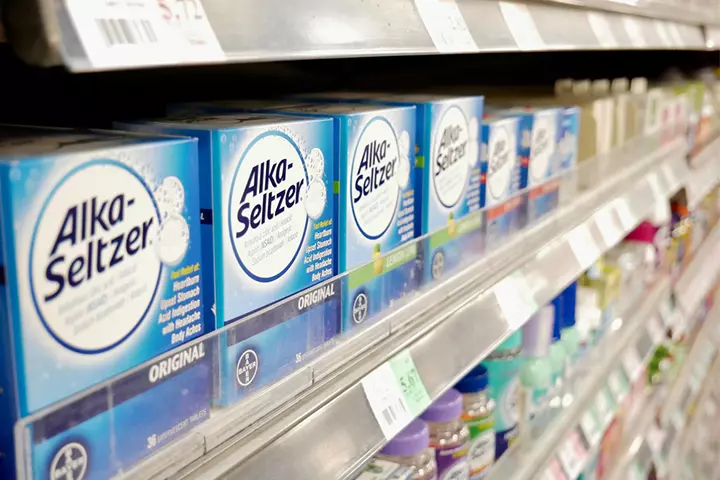
The following medications are given for indigestion in children (6):
- Antacids neutralize stomach acid and could help relieve indigestion symptoms. Alka Seltzer and Tums are examples of antacids.
Image: Shutterstock
- HistamineiChemicals released by the body during an allergic reaction blockers help reduce indigestion symptoms by reducing acid production and are available under brand names, such as Zantac and Pepcid.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) block stomach acid production. Omeprazole and Lansoprazole are examples of PPIs.
- Antibiotic therapy is required for H.pylori infection (triple therapy) and other bacterial infections that cause indigestion.
- ProkineticsiAgents or medications that help promote the motility of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract , such as metoclopramide and domperidone, help control acid reflux to the esophagus and also facilitate faster emptying of the stomach contents. These are useful in the treatment of functional dyspepsia (7).
Antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs
are required for the treatment of anxiety-related indigestion. Anxiety-related indigestion may require referral to a pediatric psychologist for psychotherapy along with medication.
Although many of these drugs are available over-the-counter, it is recommended to get a pediatrician’s prescription for the exact dosage and type of treatment, based on your child’s conditions. It is essential as prolonged or incorrect dosage of these medications could trigger other issues, such as constipation or appetite loss.
 Be watchful
Be watchfulNote: Pain relievers and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Advil (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen) should not be given for indigestion. These may worsen the condition (8).
Home Remedies For Indigestion In Children
Home remedies and lifestyle modifications are useful in preventing mild indigestion. Some such remedies are (9):
- Eating slowly and chewing thoroughly
- Avoiding dehydration
- Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or greasy foods, carbonated drinks, chocolates, processed foods, junk foods, etc.
- Regular physical activity and healthy weight
Image: IStock
- Reducing stress and anxiety by engaging your kid into more fun events and relaxation techniques
- Change in medications that are causing indigestion after discussion with the pediatrician.
 Quick tip
Quick tipAlternative medicines and complementary treatments such as herbal therapy and specific psychotherapies may be useful in some cases. You should discuss the effectiveness and safety of these treatment methods with your child’s doctor before trying them.
Preventing Indigestion In Children
Indigestion due to intake of certain medicines, foods, or drinks can be prevented by avoiding them. Eating several small meals a day and avoiding late-night eating can help reduce indigestion.
You may also encourage your child to have regular physical activity and choose healthy foods for better digestive health (10). Seeking medical care earlier can help prevent the worsening of the underlying cause of indigestion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is milk good for indigestion?
Skimmed or non-fat milk can act as a temporary layer between the stomach’s lining and its contents. It can thus provide immediate relief for children suffering from acidity (11).
2. Is banana good for indigestion?
Banana is alkaline and can help dilute the strong acids in the stomach. If your kid is experiencing heartburn or acid reflux, bananas may help curb the discomfort (11).
3. Can drinking water help with indigestion in kids?
Giving your child plenty of water and other fluids may help make their bowel movements regular. In addition, it aids in easing symptoms of indigestion (12).
4. Will indigestion go away on its own?
Mild cases of indigestion may resolve on their own (13). However, severe symptoms may require medical intervention.
Indigestion in children is a symptom of an underlying issue; hence its duration depends on the cause. The causes of indigestion or dyspepsia in children may include celiac disease, stomach ulcers, peptic ulcers, or a few gastrointestinal infections. In some cases, indigestion may be triggered by certain foods or a few lifestyle patterns. Identifying these lifestyle factors and changing them could help reduce indigestion, making the child feel better. However, if it is frequent or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, consult a pediatrician for prompt medical attention.
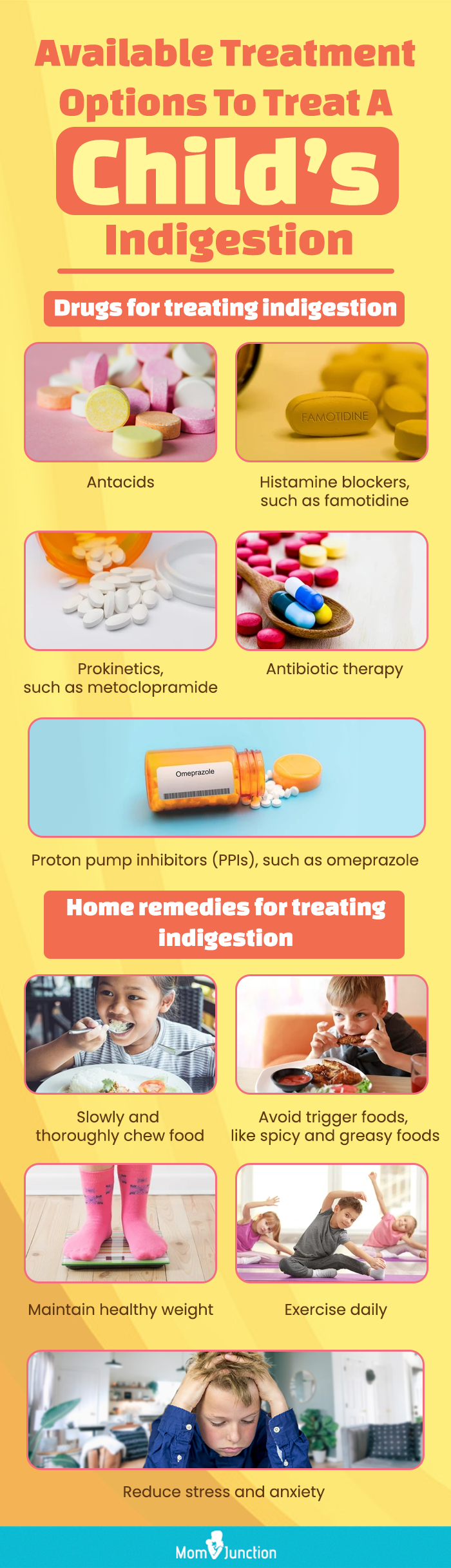
Infographic: Drug Treatments And Home Remedies For Children’s Indigestion
Indigestion in children is a frequently occurring condition that gives your child stomach pain and missed school days. Therefore, as a parent, you must always be prepared to manage this condition in your child. Keep the infographic below handy to deal with it right away. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Key Pointers
- Indigestion or dyspepsia can occur occasionally or regularly in kids of any age, depending on the underlying cause.
- Typical indigestion symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, burping, gurgling or churning stomach, acid reflux, heartburn, and nausea.
- Severe symptoms of dyspepsia that need emergency care include swallowing issues, shortness of breath, Hematemesis (vomiting of blood) or “coffee grounds” vomit, cold sweats, and Melena (black tarry stools).
- Fast food, overeating, spicy food, meals high in fiber, caffeinated or carbonated beverages, some medications, stress and anxiety, and secondhand smoking can all induce indigestion in children.
- GERD, Gastritis, Peptic Ulcer, Infections, Celiac disease, and Intestinal Obstruction are conditions and disorders that can cause severe indigestion in children.
- Simple home treatments and dietary changes can help prevent mild dyspepsia.
- Encourage children to engage in regular physical activity and eat wholesome foods for better digestive health.
Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
References
1. Symptoms & Causes of Indigestion; The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
2. Indigestion; The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
3. Indigestion – causes, treatment; Southern Cross Medical Library
4. Maria Teresa Bardella, et al., Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients With Dyspepsia; The Journal of the American Medical Association
5. Oralia V. Bazaldua and F. David Schneider, Evaluation and Management of Dyspepsia; The American Academy of Family Physicians
6. R. Christopher Harmon; Evaluation and management of dyspepsia; The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
7. Young Joo Yang, et al., Prokinetics for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: Bayesian network meta-analysis; The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
8. Indigestion (Dyspepsia); The American Academy of Family Physicians.
9. Indigestion; British international healthcare provisioning and multi-insurance group
10. Treatment of Indigestion; The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
11. GERD Diet: Foods That Help with Acid Reflux (Heartburn); Johns Hopkins Medicine
12. Indigestion in Children: Care Instructions; Kaiser Permanente
13. Indigestion; NHS Inform
Read full bio of Dr. Richard Mario Lurshay
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Anindita Ghatak








_in_kids_and_remedies_illustration.jpg.webp)