Image: ShutterStock
A child’s linear growth depends on their genetic makeup. Hence, they can only attain a certain height no matter how much they try. However, it is often said that some foods can help increase a child’s height. So are there any foods to increase height in kids? Well, there are no foods that can increase your child’s height beyond their genetic potential. However, adding certain foods to your child’s well-balanced diet can help them reach their full potential height with ease. Besides, these foods can offer nutrients to promote a child’s overall development. So, read on as we give you an insight into foods that can help children grow taller and reasons for children to not grow in height.
Can A Child’s Height Be Increased?
A child’s height mostly depends on the height of their parents and other close relatives.
Children grow at their own pace, and the rate of their height growth can significantly increase during puberty. After puberty, both boys and girls are likely to gain two inches (five centimeters) in height every year (1). However, the final, adult height of the child can depend on several factors, including genetics that plays a significant role (2).
However, the lack of nutrition could hinder the child’s growth and prevent them from attaining the average height for their age (3). Therefore, providing nutrient-rich foods is essential to help the child attain the right height.
 Did you know?
Did you know?Nutrients Required To Help A Child Grow Taller
During growth years, children need a well-balanced diet and exercise for their overall growth. There are some specific nutrients that are required in increased amounts to ensure an increase in height.
- Protein: The reference value for protein intake is 0.9 g/kg/day for boys (3-18 years) and girls (3-15 years) (4). Ensure to provide the recommended amount from a variety of sources, especially those with high protein content.
- Carbohydrates: Increased calories are required for children to grow. Thus, a balanced carbohydrate intake from complex carbohydrate sources must be consumed. Whole grains and millets are some of the healthy sources. Avoid simple carbohydrates, like those from sugary food items, since it could increase the risk of childhood obesity.
- Vitamins: All vitamins are essential for growth and sustenance. However, some specific vitamins, such as vitamin D and vitamin B-complex, can impact your child’s height directly. Thus, ensure to meet the recommended intake of all the vitamins.
- Minerals: Minerals like calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron, zinc, manganese, and fluoride are essential for the growth of your child. Several fruits and vegetables are rich in minerals, along with legumes, meat and dairy products. An adequate intake of minerals help promote healthy growth and height-increase.
 Be watchful
Be watchfulIf the daily requirement of these nutrients is not met, the chances of growth stunt may increase . Growth stunting could occur in extreme cases of nutritional deficiencies. If children are unable to consume enough of these nutrients through their diet alone, supplements may be recommended.
Best Foods To Increase A Child’s Height
A balanced diet with enhanced intake of certain nutrients is important to promote growth in children
. Below is a list of some foods that you could add to your child’s diet on a regular basis to ensure optimum growth in height (and weight).
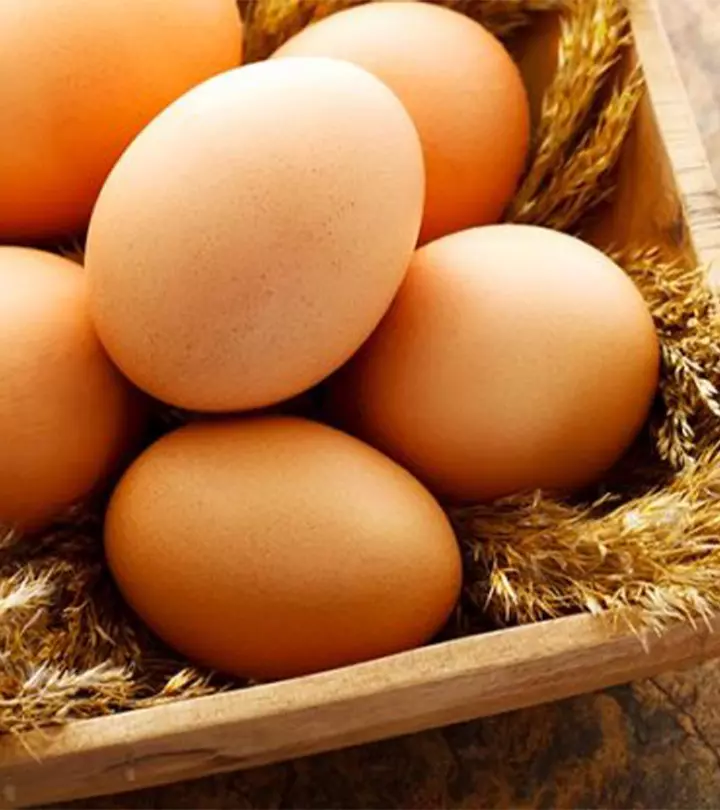
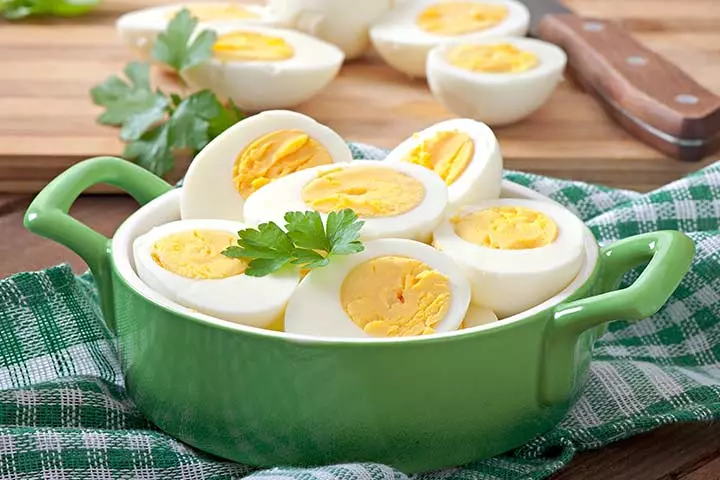
1. Eggs
An egg provides almost 6.5 grams of protein and has almost all the essential amino acids in it (4) (5). This makes egg a source of complete protein that is required for skeletal growth of children (6). Besides, it has several other nutrients like vitamin D, phosphorus, omega-3 fatty acids, selenium, and iodine that helps in overall growth and development of children (7).
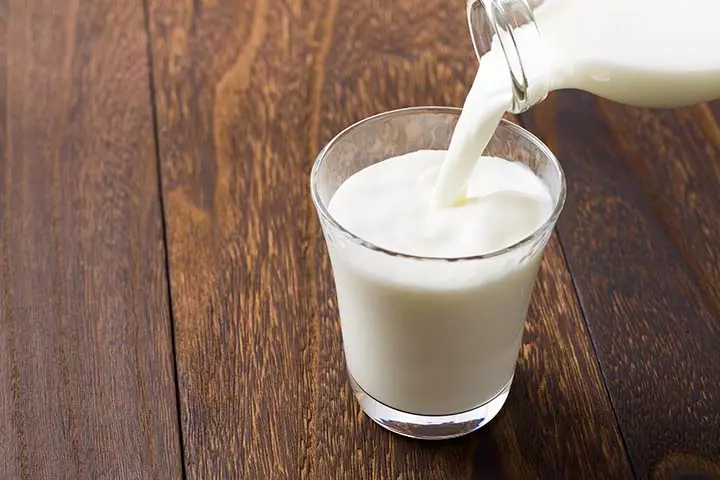
2. Milk
The protein, vitamins such as vitamin-D and minerals such as potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in whole milk support bone development (8). Whole milk has more nutrients than the skimmed versions. Thus, children should be served whole milk or products made of whole milk unless they are advised otherwise due to weight issues such as childhood obesity.
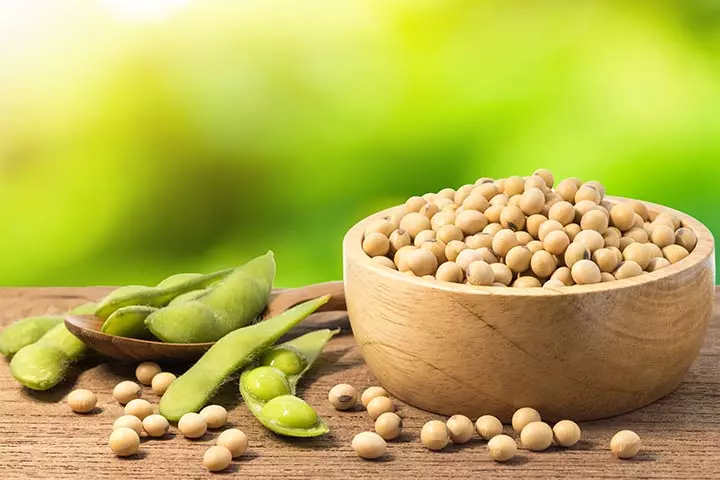
3. Soybean
Consider including products made from soybean in the child’s diet. A few examples of soybean products are soy flour, soy chunks, tofu, and soy milk. Soybeans are high in protein that is considered equivalent to animal protein (9). Soy products like tofu and soy milk are also high in calcium. This makes an excellent protein source for vegans. Regular consumption of soy may help improve bone health (10).
 Point to consider
Point to consider4. Red meat
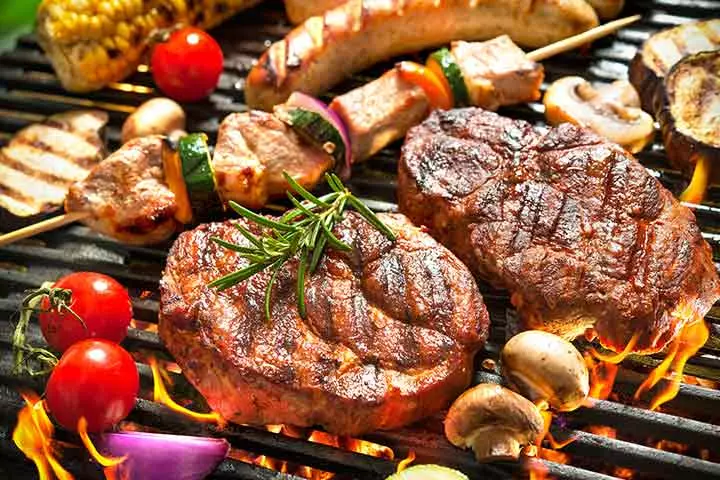
Red meat is rich in protein and several micronutrients, including iron (11) that is essential to prevent anemiaiA condition where the body lacks red blood cells to transport oxygen to body tissues . Anemia, in turn, can cause weakness and may affect a child’s growth. However, red meat is also rich in saturated fat, so it is good to limit its consumption to a moderate level. Trim all the visible fat before cooking to lower the total fat content in red meat further.
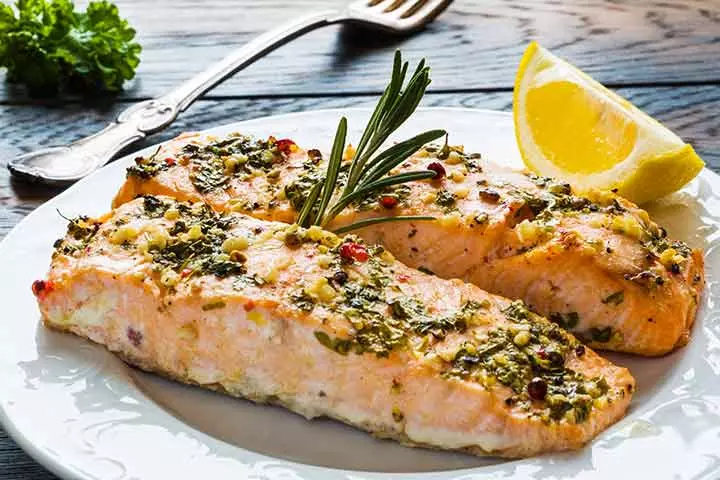
5. Lean meat
Fish and skinless chicken are ideal options for lean meat, which is rich in protein but low in saturated fat. Other lean meat options such as turkey can also be served to children.
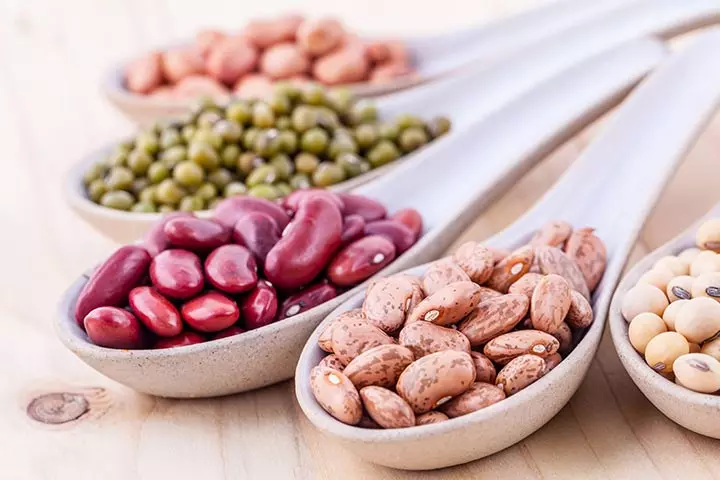
6. Legumes
Legumes, including lentils, black beans, pinto beans, red kidney beans, are rich in protein and low in fat content (12). Most legumes contain a good amount of calcium and dietary fiber, essential for a growing child. You can try adding legumes to your kids’ meals for a protein, nutrient packed diet.
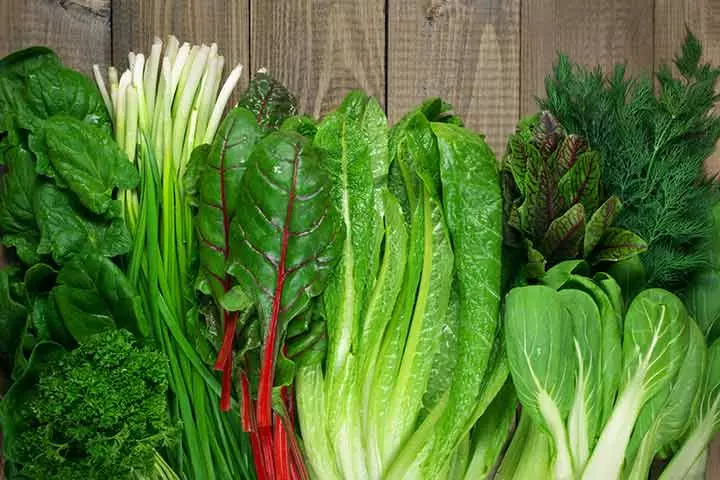
7. Leafy vegetables
Leafy vegetables are a good source of calcium for children who do not consume milk due to lactose intolerance or dietary choices (13). Leafy vegetables are also a good source of vitamin K that is essential for bone health (14). Some of the calcium-rich leafy vegetables that can be added to your children’s daily diet are turnip greens, bok choy, kale, amaranth, collard greens, and watercress.
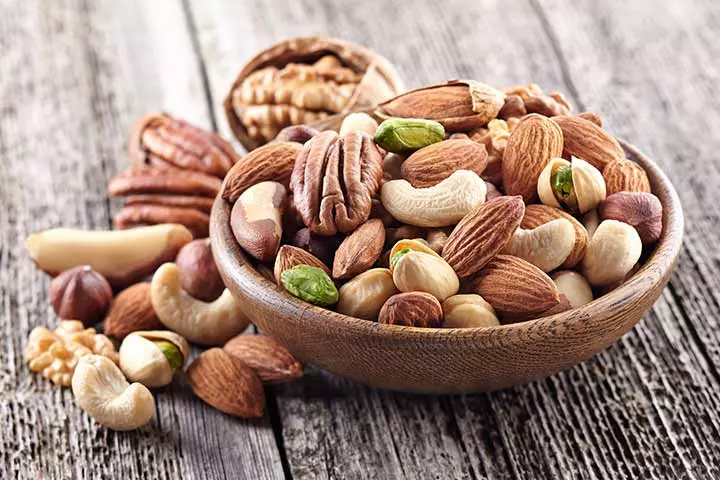
8. Nuts
Nuts contain a mix of protein and calcium (15). Besides, they provide good amounts of omega-3 fatty acids that may improve bone and joint health (16). You can consider adding an assortment of nuts to the child’s diet. A few examples of nuts that contain the right amount of protein are almonds, pistachios, and walnuts.
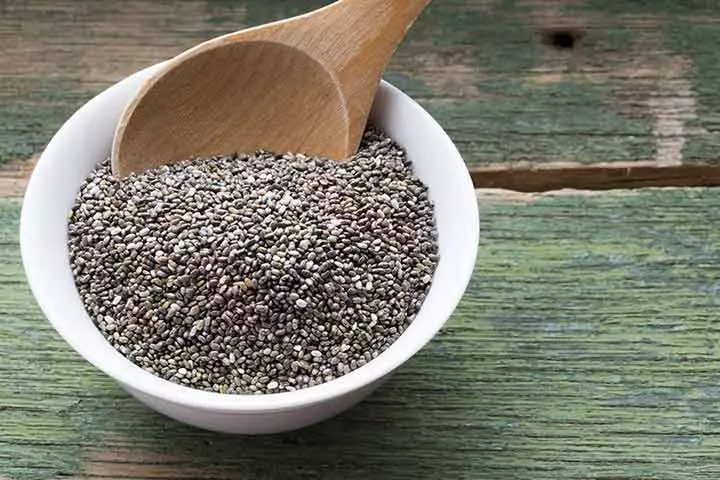
9. Seeds
Most seeds contain protein, and some of them even contain minerals such as calcium. For example, chia seeds contain calcium (17). They are also high in omega 3 fatty acids and fiber. Other seeds like sesame seeds can be roasted or used raw in salads.
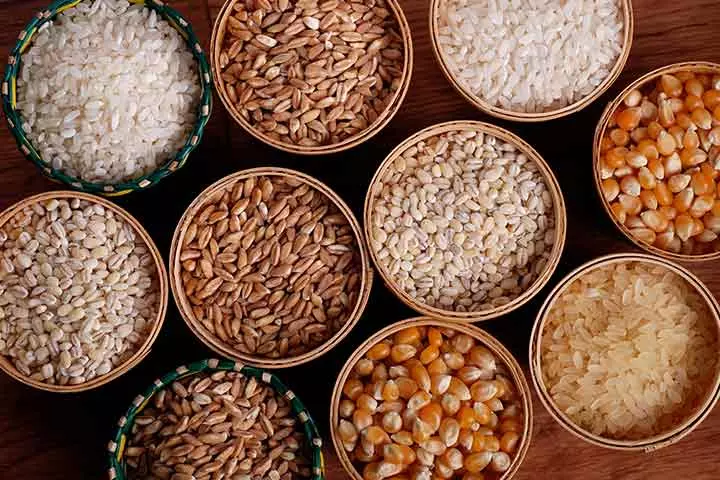
10. Grains
Grains may not contain much calcium but can be a source of magnesium, a mineral that plays an important role in promoting bone health (18). Include an assortment of grains in your child’s diet. Use whole grain that comes with the husk, a good source of fiber. Some of the whole grains that are a good source of calcium and magnesium are oats, barley, and pseudocerealsiPlants that produce edible seeds, which are nutritious alternatives to traditional grains but are not in the grass family (Poaceae) like buckwheat and quinoa.
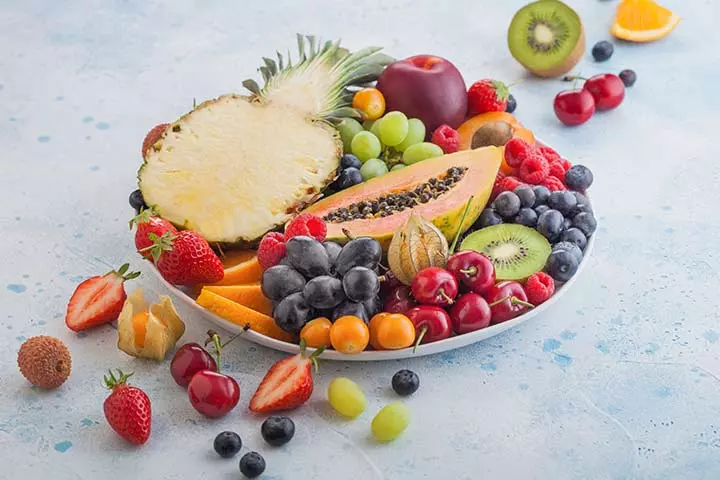
11. Mineral-rich fruits
According to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2021, nearly one-third (32%) of children between one and five years did not eat fruit daily in that year. Generally, fruits are not often associated with minerals, but some fruits contain an adequate amount of calcium and other minerals required for the healthy growth of the bones. Examples of fruits with calcium content are orange, apricot, kiwi, and pineapple (19) (20) (21) (22). So, include a wide variety of fruits in your children’s diet to attain optimum growth.
A well-planned, balanced diet, and regular exercise could help your child to grow in length. Moreover, it would also help keep chronic conditions like childhood obesity at bay. However, in case you do not see any results, visiting a doctor would be advisable.
Reasons Why A Child Is Not Growing In Height
Your child’s height is an important marker of nutritional status and physical development (23). Besides genetic makeup and diet, there could be several other reasons for a child to exhibit delayed growth. Below are some possible reasons that are worth a check.
- Constitutional growth delay: Children with this condition grow at a normal rate. However, they are shorter than average. They usually exhibit delayed bone growth and tend to reach puberty late. Due to this, such children have a below-average height in the teenage years, but then they tend to catch up with their peers in adulthood (24).
- Growth hormone deficiency: Growth hormone (GH) is a hormone that helps in normal growth and development. In cases where a child has partial or complete GH deficiency, stunting is observed (25).
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Hypothyroidism: It is a common endocrineiThe system where glands produce hormones that controls all bodily functions, including metabolism and reproduction disorder caused by an underactive thyroid glandiA small gland located in the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels . In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient thyroid hormone, thus leading to conditions such as fatigue, weight gain, decreased growth, etc. (26).
- Turner syndrome: It is one of the common genetic conditions in girls caused by a complete or partial absence of the X chromosomeiA genetic structure found in cells that contains DNA and helps determine an organism's characteristics and traits during embryonic development. The most prominent features of the condition are short height and premature ovarian failure (27).
Foods That Stunt Growth
Studies suggest that consuming ultra-processed foods that are laden with sugar and fat may have a negative effect on the growth of children. A study conducted on young rats revealed that consumption of such foods led to growth retardation, characterized by lesions in the tibial growth plates. This phenomenon was associated with a significant decrease in bone mineral density and structural deterioration. Consequently, the entire bone exhibited inferior mechanical performance, elevating the risk of fractures (28). These findings underscore the severe impact of consuming ultra-processed foods on the developing skeleton, emphasizing the need for awareness and dietary adjustments to promote healthy skeletal development in children. Ultra-processed foods include items like ice cream, ham, sausages, crisps, factory-made bread, breakfast cereals, biscuits, fizzy drinks, fruit-flavored yogurts, and instant soups (29).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What should be done to promote height in children?
To promote height in children, it is important to ensure they receive proper nutrition. Therefore, it is recommended to follow dietary guidelines suitable for the child’s age and ensure they consume a balanced diet. Growth in children can be promoted by following good eating practices from a young age (30).
2. Can medicine increase children’s height?
Medical treatment can be a viable option to increase a child’s height if the growth stunt is caused by a medical disorder. Endocrine disorders and growth hormone deficiency are some conditions that may lead to stunted growth. In such cases, doctors may recommend daily or weekly hormone replacement therapy to promote height and help children reach their full growth potential (31).
3. Does growth hormone increase height in children?
Dr. Shoaib Malik, a preventative care specialist from New York City Metropolitan Area, opines, “In children, growth hormone deficiency can result in short stature. In such cases, treatment with growth hormone can increase the child’s height. However, it is important to note that growth hormone treatment is only recommended for children with growth hormone deficiency and not for those with normal hormone levels.”
A child’s height is mostly dependent on their genetic makeup, and no matter how much one exercises, there is only so much one can do to increase their height. However, some foods can help in increasing a child’s height. A child needs a well-balanced diet with essential nutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to attain proper growth. Milk, eggs, soybean, red meat, etc., are some examples of healthy foods that can help your child attain the maximum possible height. Despite eating a well-balanced diet, there may be certain underlying conditions if your child is not growing in height. You can contact your healthcare provider or a child nutritionist to get the necessary help for your child’s growth and development.
Infographic: Best Foods To Increase A Child’s Height
A well-balanced diet is essential to ensure a child’s proper growth and development. However, if you are worried that your little one is not attaining the recommended height at their respective age, fret not! In the following infographic, we have listed a few food items you might include in your child’s diet to help them grow. Read on! Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Key Pointers
- The height of your child usually depends upon your genetic makeup. Once they attain puberty, your child is likely to gain two inches in height every year.
- Lack of nutrients is also a factor that can impact your child’s growth.
- A growing child needs to engage in a well-balanced diet and exercise for their overall growth.
- The food that they consume must be rich in proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
- Foods like eggs, milk, red meat, legumes, leafy greens, nuts, and grains must be consumed.
- Besides genetic makeup and height, factors like delayed bone growth, growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, and Turner syndrome could also be responsible for your child’s lack of height.
Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Explore this video to uncover the top ten foods that can assist in achieving increased height. Learn which foods can help you reach your height goals.
References
1. Physical changes during puberty; American Academy of Pediatrics
2. Is height determined by genetics?; U.S. National Library of Medicine
3. Short stature; U.S. National Library of Medicine
4. Agneta Hornell et al.; Protein intake from 0 to 18 years of age and its relation to health: a systematic literature review for the 5th Nordic Nutrition Recommendations; National Center for Biotechnology Information
5. Michael J. Puglisi* and Maria Luz Fernandez; The Health Benefits of Egg Protein; NCBI
6. Jamie I. Baum et al.; The effect of egg supplementation on growth parameters in children participating in a school feeding program in rural Uganda: a pilot study; National Center for Biotechnology Information
7. 5 reasonHow to increase children’s heights to add eggs to the menu; University of Utah
8. Michael J. Puglisi* and Maria Luz Fernandez; , Effects of dairy products consumption on health; National Center for Biotechnology Information
9. Soy; U.S. National Library of Medicine
10. A. J. Lanou, Soy foods: Are they useful for optimal bone health?; National Center for Biotechnology Information
11. Macronutrients & Micronutrients; Pomana College
12. All about beans nutrition, health benefits, preparation and use in menus; North Dakota State University
13. Calcium: What’s best for your bones and health?; Harvard T.H. Chan
14. Hip fractures and leafy vegetables; Tufts University
15. How to eat nuts the healthy way; Harvard Medical School
16. Naroa Kajarabille et al.; A New Insight to Bone Turnover: Role of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids; National Center for Biotechnology Information
17. Chia Seeds | The Nutrition Source; HSPH
18. Charles T Price et al.; Essential Nutrients for Bone Health and a Review of their Availability in the Average North American Diet; NCBI
19. Oranges, raw, navels; USDA
20. Apricots, raw; USDA
21. KIWIFRUIT; USDA
22. Pineapple juice, canned, not from concentrate, unsweetened, with added vitamins A, C and E; USDA
23. Fafard St-Germain and Siddiqi; The Relation Between Household Food Insecurity and Children’s Height in Canada and the United States: A Scoping Review.; National Center For Biotechnology Information
24. Constitutional Growth Delay; National Center For Biotechnology Information
25. Growth Hormone Deficiency; Boston Children’s Hospital
26. Hypothyroidism; The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
27. Kateri McCarthy and Carolyn A Bondy; Turner syndrome in childhood and adolescence; National Center For Biotechnology Information
28. Janna Zaretsky et al.; Ultra-processed food targets bone quality via endochondral ossification; Nature
29. Ultra-processed foods: how bad are they for your health?; British Heart Foundation
30. Poor Diets Damaging Children’s Health Worldwide; warns UNICEF; UNICEF
31. Growth Problems; Boston Children’s Hospital
32. Vitamins and Minerals for My Child; Indian Academy of Pediatrics
Read full bio of Charmaine Dominguez
- Dr. Shoaib Malik is a physician with over 10 years of experience. He currently works at Prime Health of New Jersey and specializes in primary care and chronic disease management, including hypertension and diabetes. Dr. Malik studied medicine at Medical University of the America.
 Dr. Shoaib Malik is a physician with over 10 years of experience. He currently works at Prime Health of New Jersey and specializes in primary care and chronic disease management, including hypertension and diabetes. Dr. Malik studied medicine at Medical University of the America.
Dr. Shoaib Malik is a physician with over 10 years of experience. He currently works at Prime Health of New Jersey and specializes in primary care and chronic disease management, including hypertension and diabetes. Dr. Malik studied medicine at Medical University of the America.
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das