Image: MomJunction Design Team
Children need to be given an adequate amount of essential vitamins and minerals for healthy development during the different growth stages. One such essential nutrient is zinc. The benefits of zinc-rich food for kids are substantial as it helps build tissues and strengthens the immune system in children (1).
Zinc deficiency in the early years might cause a weakened immune system in children and increase their susceptibility to infections and other diseases (2). This, in turn, increases the morbidity and mortality rate of children.
According to scientists and health experts, a healthy child between 4 to 13 years requires an average of 5 to 8mg of zinc per day for proper development (3). If it cannot be obtained from food, it should be taken through supplements.
Read on to know more about the benefits of including zinc in your child’s diet and ways in which you can do so.
Click here to view an enlarged version of this infographic
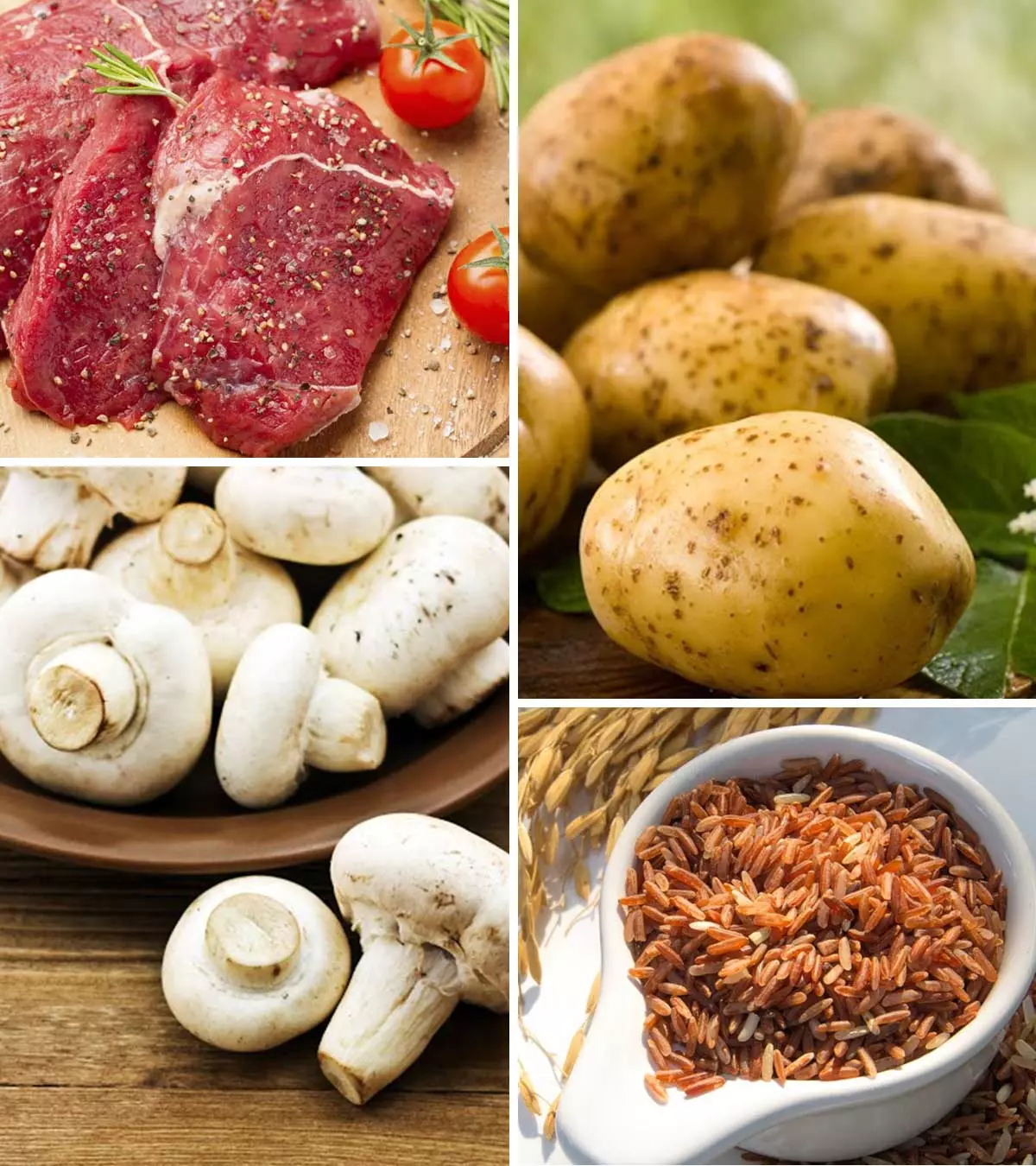
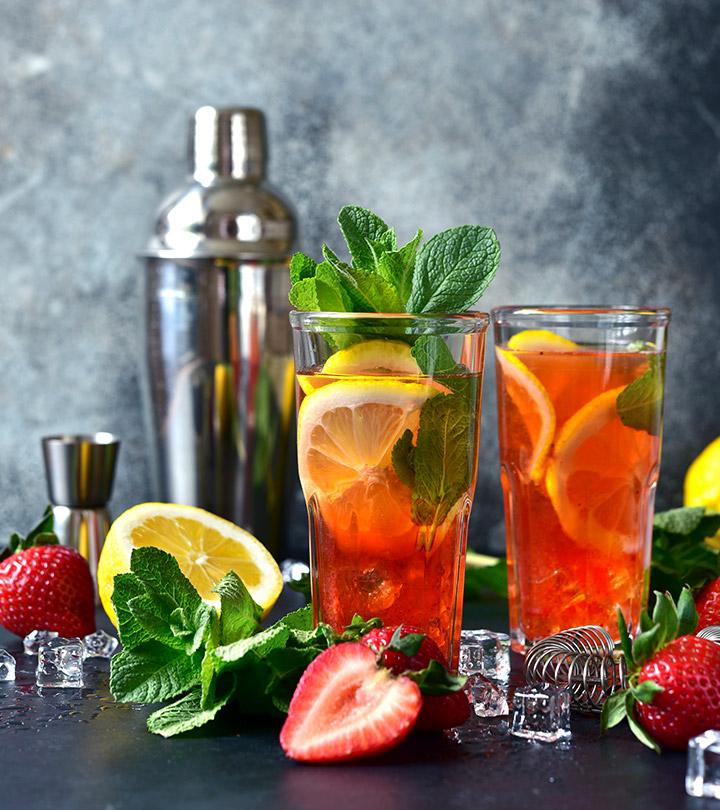
What Are Some Zinc-Rich Foods?
Image: Shutterstock
As per medical research, it is found that adding zinc to the diet of young children can be highly beneficial for their overall health.
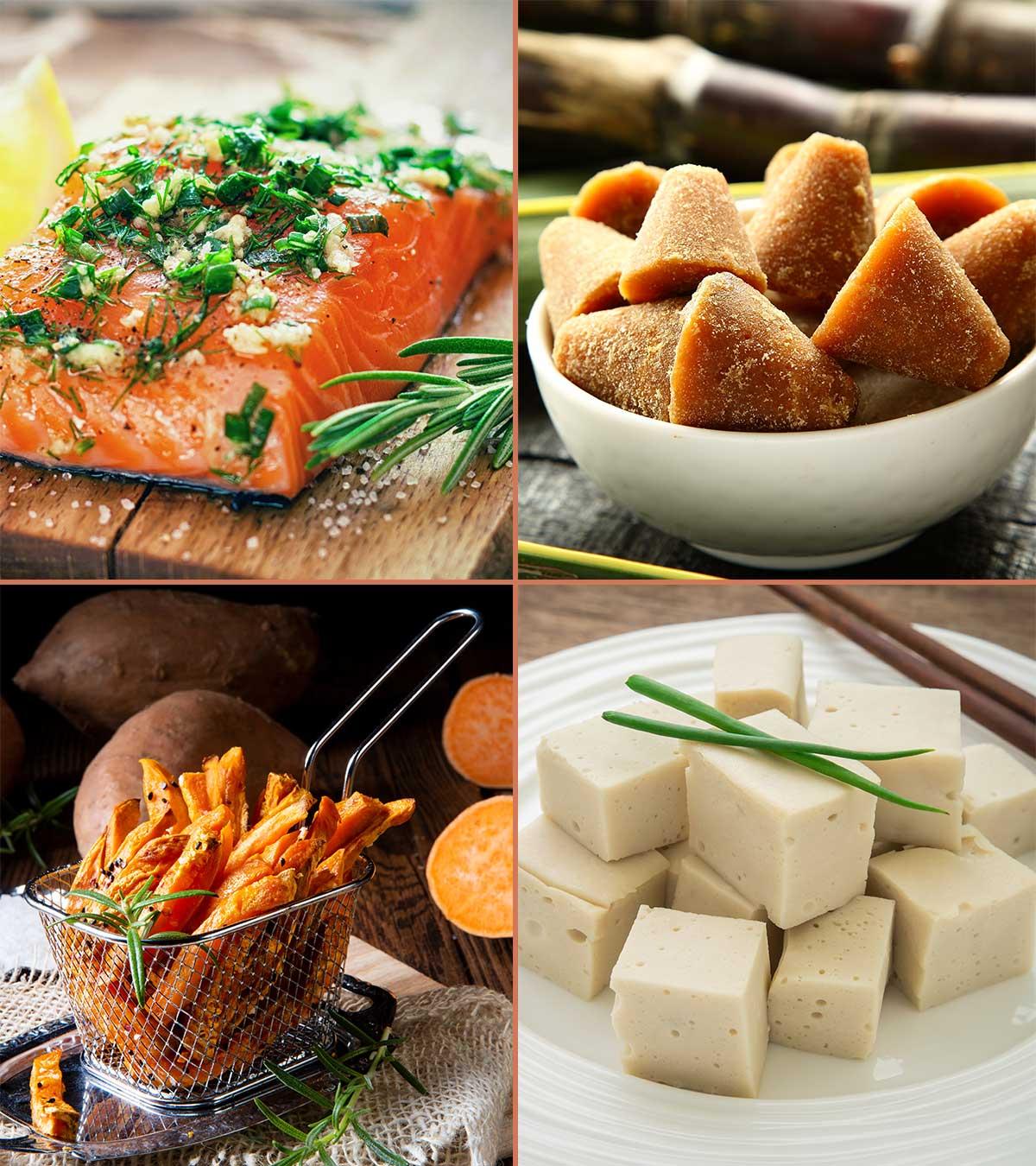
Zinc for children is available from the following food items (4):
- Red Meat
- Seafood like oysters and other shellfish
- Potatoes along with their skin
- Beans
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Mushrooms
- Whole grain cereals
- Fortified cereals
- And a small portion in breast milk also.
Some of these foods are calcium-rich foods while some are iron-rich foods. Together, these foods make your child’s diet more nutritious. You can use these foods to make healthy snacks for your child as well.
 Did you know?
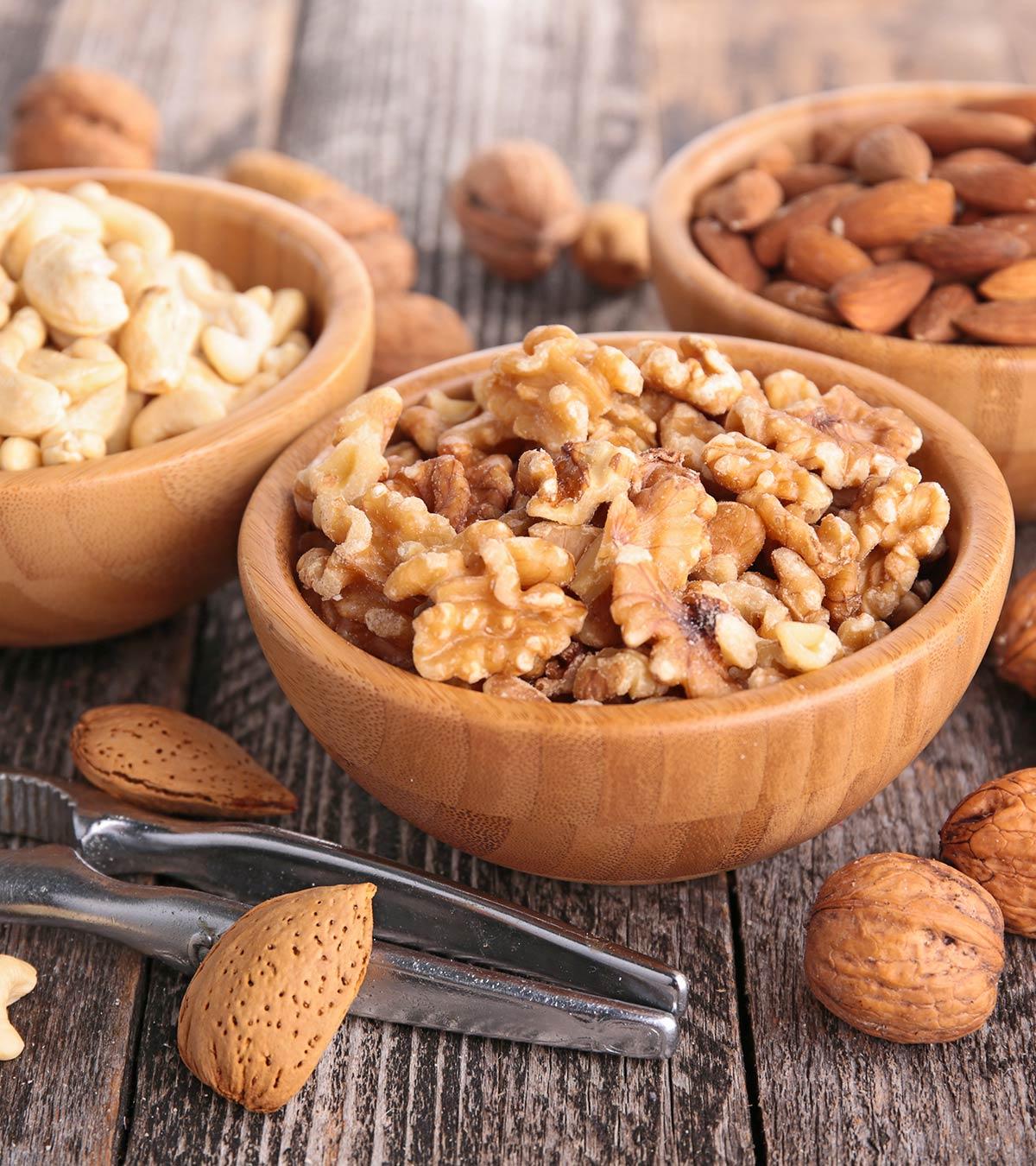
Did you know?What Are The Benefits Of Zinc For Children?
Image: IStock
A small amount of zinc can produce favorable results for your children. Do take a look at its innumerable advantages mentioned below (4):
- Zinc is critical for normal growth as well as the development of the reproductive organs in the body.
- Zinc helps improve the immune system of your body and thereby protects you from various diseases.
- When children do not get required zinc proportions in the body, it can lead to reduced memory, learning disabilities and also reduces the concentration span of the mind.
- Zinc helps treat stunted growth and severe diarrhea in children. Zinc therapy is given for 14 days in treatment of diarrhea to all children.
- It also helps in fighting against common diseases such as cough, cold, and ear infections. At the same time it can fight against diseases caused by parasites like malaria.
- It also plays an important role in treatment of ADHD (Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), tinnitus, which causes bell-like sound in ears, critical head injuries, eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, Down syndrome, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- And lastly, zinc can help in treating eye disease, AIDS, asthma, diabetes, high blood pressure, etc.
 Did you know?
Did you know?Is Zinc Supplementation Necessary?
Image: Shutterstock
If you find a deficiency of zinc in children, it is advisable to provide your child with zinc supplements.
Zinc supplements have been proved useful when provided to children who suffered from its deficiency. There are many zinc supplements available in markets and you should consult your doctor before you start giving supplements to your kids. If your child has iron deficiency, the pediatrician might suggest iron supplements as a part of anemia prevention. They can be given with zinc supplements as they do not interfere with zinc absorption.
 Point to consider
Point to considerIs Too Much Zinc Harmful To Your Child?
Consuming too much zinc can harm your child. Excessive zinc supplements might cause feelings of sickness, dizziness, headaches, tummy troubles, throwing up, and loss of appetite. When taken for an extended time, it might weaken the body’s defenses, lower the good cholesterol, and decrease copper levels. High doses of supplemental zinc can also interfere with magnesium absorption. It’s crucial to be mindful of daily upper limits, considering zinc intake from all sources, including foods, beverages, supplements, and medications. The table below outlines age-specific upper limits (3):
| Ages | Upper Limit |
|---|---|
| Up to 6 months | 4mg |
| 7 to 12 months | 5mg |
| 1 to 3 years | 7mg |
| 4 to 8 years | 12mg |
| 9 to 13 years | 23mg |
| 14 to 18 years | 34mg |
| Adults | 40mg |
However, these limits may not apply to individuals under medical zinc supplementation supervised by a doctor.
Caution When Using Zinc Supplements For Children
Image: IStock
Many scientists believe that when zinc is taken in more than adequate proportions it is not suitable. They believe that if zinc is excess in the body it can cause similar problems which are caused due to deficiency.
- So when you opt for supplements of zinc be careful regarding its dosage and its content.
- It is often found that zinc, which is metal, is commonly found together with another metal called cadmium. When cadmium is consumed in excess, it can result in kidney failure in the long run (5).
- Essentially when you take supplements they are often found with concentrated cadmium too and thus may not be beneficial.
- Thus when you look for supplements always consider the ones which are zinc- gluconate. It is believed that the combination of zinc gluconate has the lowest level of cadmium in it (6).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. At what age can kids have zinc?
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, zinc-rich food should be given to children as young as six months old to meet their nutritional needs. Children between the ages of seven and 24 months need 3mg of zinc every day (4).
2. Can a child have too much zinc?
It is unlikely to have an overdose of zinc from solids alone. However, if your child is eating solids and taking zinc supplements and complaining of symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, appetite loss, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, or headaches, it may indicate an overdose of zinc (4).
3. Are there any differences in the amount of zinc needed by boys versus girls?
The recommended dietary allowances for zinc among boys and girls remain consistent from birth to 14 years (2) (7).
4. Are there any food allergies associated with zinc-rich foods?
Zinc is available in varied food sources, which may be a potential allergen, depending on individual factors associated with the child. Allergies to these foods may also affect zinc absorption (7).
Zinc-rich foods for kids are essential for immunity and the strength of tissues. Red meat, shellfish, potatoes, nuts, beans, and whole grains are rich dietary sources of zinc. Younger children can get the required amounts of zinc from breast milk. Increased infections are one of the signs of zinc deficiency due to weakened immune system functions. Also, children with zinc deficiency have memory problems, learning issues, and concentration problems. You may give zinc supplements as per the pediatrician’s recommendations since excess amounts of zinc can lead to complications.
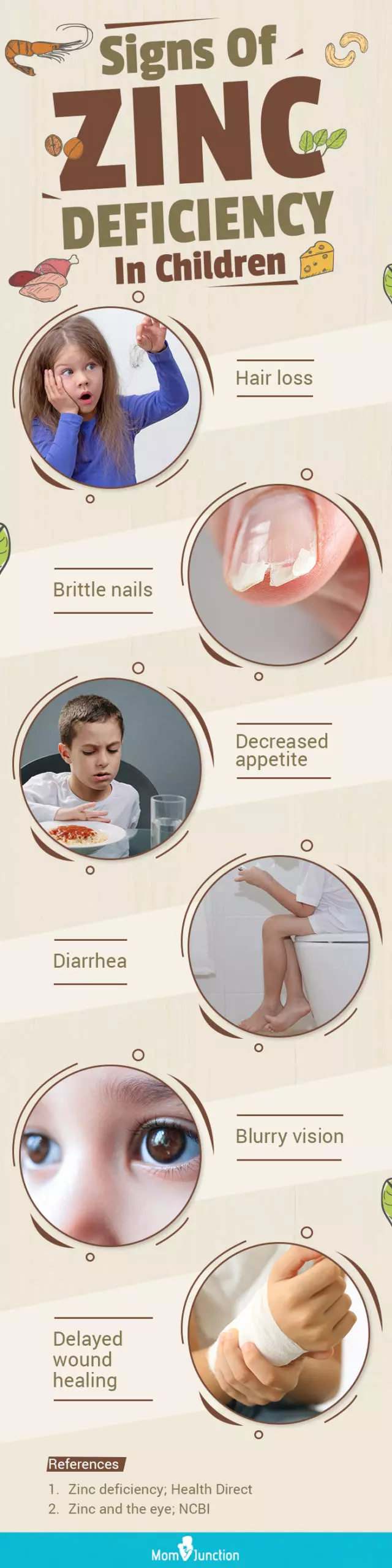
Infographic: Symptoms Of Zinc Deficiency In Children To Watch Out
Zinc is essential for healthy growth and development during childhood and adolescence. Zinc deficiency is related to poor diet and reduced absorption due to an illness. This deficiency can be treated by consuming a diet rich in this mineral. Learn about critical signs of zinc deficiency in children in the infographic below.
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Key Pointers
- Zinc is beneficial for children’s growth and overall development.
- It contains vital minerals and vitamins that strengthen tissue and the immune system.
- A balanced diet rich in zinc from dairy products, whole grains, nuts, and other sources is crucial for daily intake.
- Parents should be cautious about dosing zinc supplements to avoid potential health risks to their children.
Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Make sure your kids get the essential nutrient zinc! Learn how to ensure they get enough for healthy growth and development.
References
- Zinc.
https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/supplement/zinc - Zinc Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/ - Zinc Fact Sheet for Consumers.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-Consumer/ - Zinc
https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/infantandtoddlernutrition/vitamins-minerals/zinc.html - Mehrdad Rafati Rahimzadeh et al.; (2017); Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5596182/ - C A Krone et al.; (2001); Cadmium in zinc-containing mineral supplements.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11474903/ - The Role of Zinc: It’s More Important than You Think
https://www.uml.edu/news/stories/2020/kelleher-zinc-research.aspx
Read full bio of Dr. Prakhar Nyati
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny